Dapagliflozin: What It Is, How It Works, and What Alternatives Exist
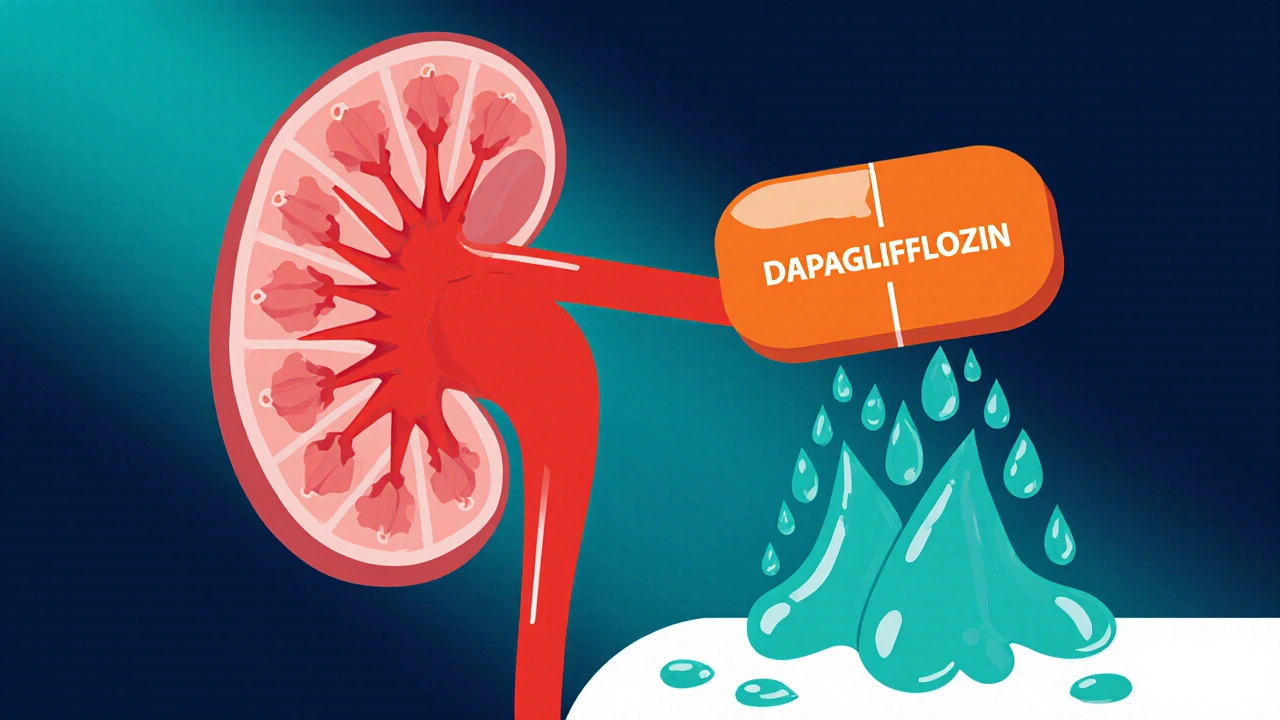
When you hear dapagliflozin, a prescription medication used to lower blood sugar in adults with type 2 diabetes and to reduce the risk of hospitalization for heart failure. Also known as Farxiga, it works by helping your kidneys flush out extra sugar through urine instead of reabsorbing it back into your bloodstream. This isn’t just another diabetes pill—it’s part of a newer class called SGLT2 inhibitors, and it’s been shown to do more than control glucose. Studies like the DAPA-HF trial proved it cuts hospital stays for heart failure, even in people without diabetes. That’s why doctors now prescribe it for heart and kidney protection, not just blood sugar.
That brings us to two other key players: SGLT2 inhibitors, a group of drugs that work like dapagliflozin by blocking sugar reabsorption in the kidneys, and heart failure, a condition where the heart can’t pump blood effectively, often worsened by long-term high blood sugar. Dapagliflozin doesn’t just treat symptoms—it changes outcomes. For someone with type 2 diabetes and early kidney damage, this drug can slow progression. For someone with heart failure, it reduces fluid buildup and improves survival. It’s not a quick fix, but it’s one of the few medications that helps multiple organs at once.
What makes dapagliflozin stand out? Unlike older diabetes drugs that force your pancreas to make more insulin or make your body more sensitive to it, dapagliflozin lets your body naturally get rid of sugar. That means less risk of low blood sugar. It also leads to modest weight loss and lower blood pressure—two extra benefits many patients appreciate. But it’s not for everyone. If you’re prone to urinary infections, dehydrated easily, or have severe kidney disease, your doctor might pick something else.
That’s where alternatives come in. Other SGLT2 inhibitors like empagliflozin and canagliflozin work similarly but have different side effect profiles. Metformin is still the first-line choice for most, but if you’ve got heart or kidney issues, dapagliflozin often joins the team. GLP-1 agonists like semaglutide are great for weight loss and blood sugar, but they’re injectable and more expensive. Dapagliflozin? It’s a daily pill with proven benefits beyond glucose.
Below, you’ll find real comparisons and practical guides—how dapagliflozin stacks up against other diabetes and heart meds, what side effects to watch for, and how it fits into broader treatment plans. Whether you’re managing diabetes, dealing with heart strain, or just trying to understand your prescription, these posts give you the clear, no-fluff facts you need.
Dapagliflozin and Neuropathy: Can It Help Prevent Nerve Damage in Diabetics?
Explore whether dapagliflozin can help prevent or slow diabetic neuropathy, reviewing mechanisms, trial data, benefits, risks, and practical usage tips.