Pharmaceutical Supply Chain: How Medicines Get to You Safely
When you pick up a prescription, you’re not just getting a pill—you’re receiving the end result of a complex, high-stakes system called the pharmaceutical supply chain, the end-to-end network that moves drugs from manufacturers to patients, ensuring safety, legality, and availability. Also known as drug distribution network, it includes makers, wholesalers, distributors, pharmacies, and regulators—all working in sync to prevent errors, counterfeits, and shortages. This isn’t just logistics; it’s public health infrastructure.
Behind every bottle of metformin or Shingrix vaccine is a trail of checks: raw materials tested, batches tracked with barcodes, storage temperatures monitored, and shipments verified at every stop. The barcode scanning, a key tool used in pharmacies to confirm the right drug, dose, and patient before dispensing system alone cuts dispensing errors by 93%. Meanwhile, the generic medicines, affordable copies of brand-name drugs approved under strict FDA standards after patents expire rely on this same chain to reach people who can’t afford originals. Without a tight supply chain, those savings disappear—and so do lives.
When a drug like clozapine carries a black box warning for agranulocytosis, the supply chain doesn’t just deliver it—it enforces monitoring rules. Pharmacies track who gets it, how often, and whether blood tests are up to date. Even something as simple as automated refills for chronic meds ties into this system, reducing missed doses by keeping the flow steady. But it’s not flawless. Patent laws, shipping delays, and price gouging can all choke the chain. That’s why regulations like the No Surprises Act and Hatch-Waxman Act matter—they’re designed to keep the system fair and functional.
What you’ll find below are real stories from inside this system: how a single error in a warehouse can lead to overdose, why grapefruit juice interacts with 85+ drugs because of how they’re metabolized, how online pharmacies use automation to keep patients on track, and why some meds get pulled from shelves overnight. These aren’t abstract policies—they’re the daily realities that keep your pills safe, legal, and effective.
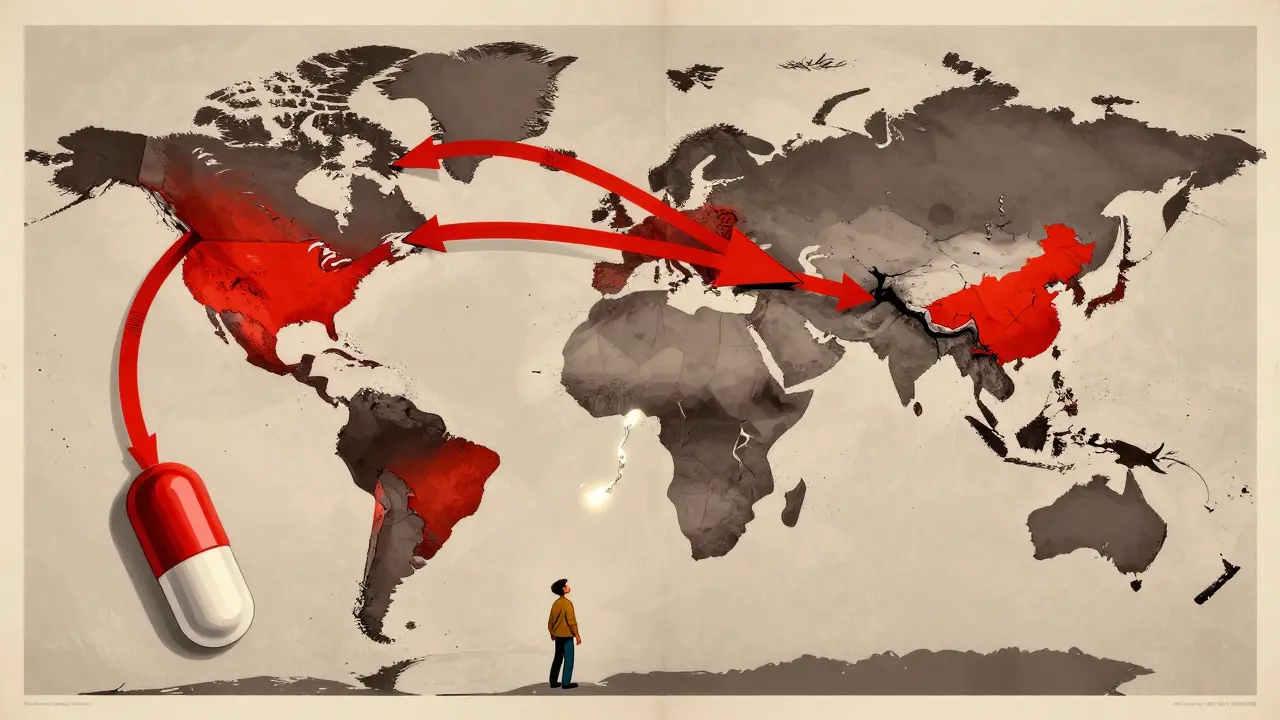
International Supply Chains: How Foreign Manufacturing Dependence Is Causing Drug Shortages in 2025
In 2025, drug shortages are worsening because 90% of active ingredients still come from just two countries. Dependence on foreign manufacturing makes supply chains fragile - and patients are paying the price.
How COVID-19 Disrupted Drug Availability and Created Lasting Shortages
The COVID-19 pandemic caused severe drug shortages and a surge in deadly overdoses. Essential medications vanished as global supply chains broke down, while illicit drugs became more potent with fentanyl. Telehealth helped some, but left others behind.